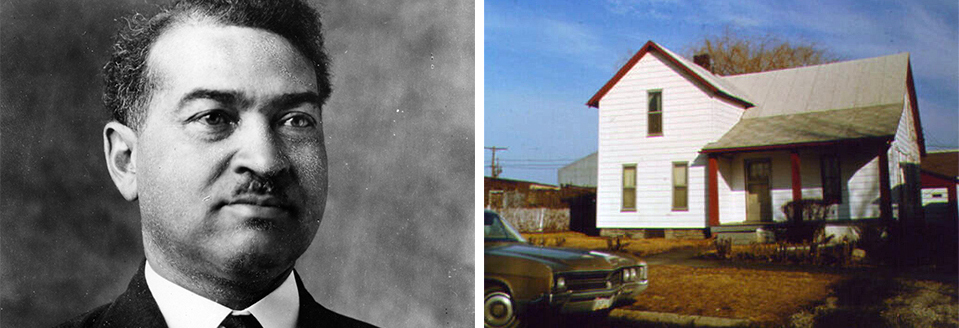
Albert R. Lee
605 N. Walnut, Champaign, IL
Albert R. Lee was born on June 26, 1874, on a farm outside of Champaign, Illinois. He attended the University of Illinois in 1894, and in 1895 he became the second African American hired at the university. He started as a messenger, but then became the clerk for the Office of the President. Lee served under six university Presidents. At a time when African Americans were not allowed to live on campus, he took it upon himself to assist them with housing and maneuvering through school, becoming known as the unofficial Dean of African American Students.
Lee was also very active in his community as a member of Kappa Alpha Psi (Beta Chapter), the Knights of the Templar Free Masons, the NAACP, and the Bethel A.M.E. Church in Champaign.
He died in 1948 and was buried in Mount Hope Cemetery in Champaign. In fall of 2018, a new tombstone was dedicated to replace the original tombstone, which had been severely damaged. The dedication event brought University officials and Champaign-Urbana residents together to recognize this unsung individual who played a pivotal role in both communities.
You can learn more about Albert R. Lee’s contributions and legacy by watching these videos from the University of Illinois:
Albert R. Lee: A Man of Substance
Albert R. Lee Portrait Dedication at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
Decade:
1870-1879
People:
- Albert Lee
Location(s):
- Champaign, Illinois
Additional Champaign Trail Sites